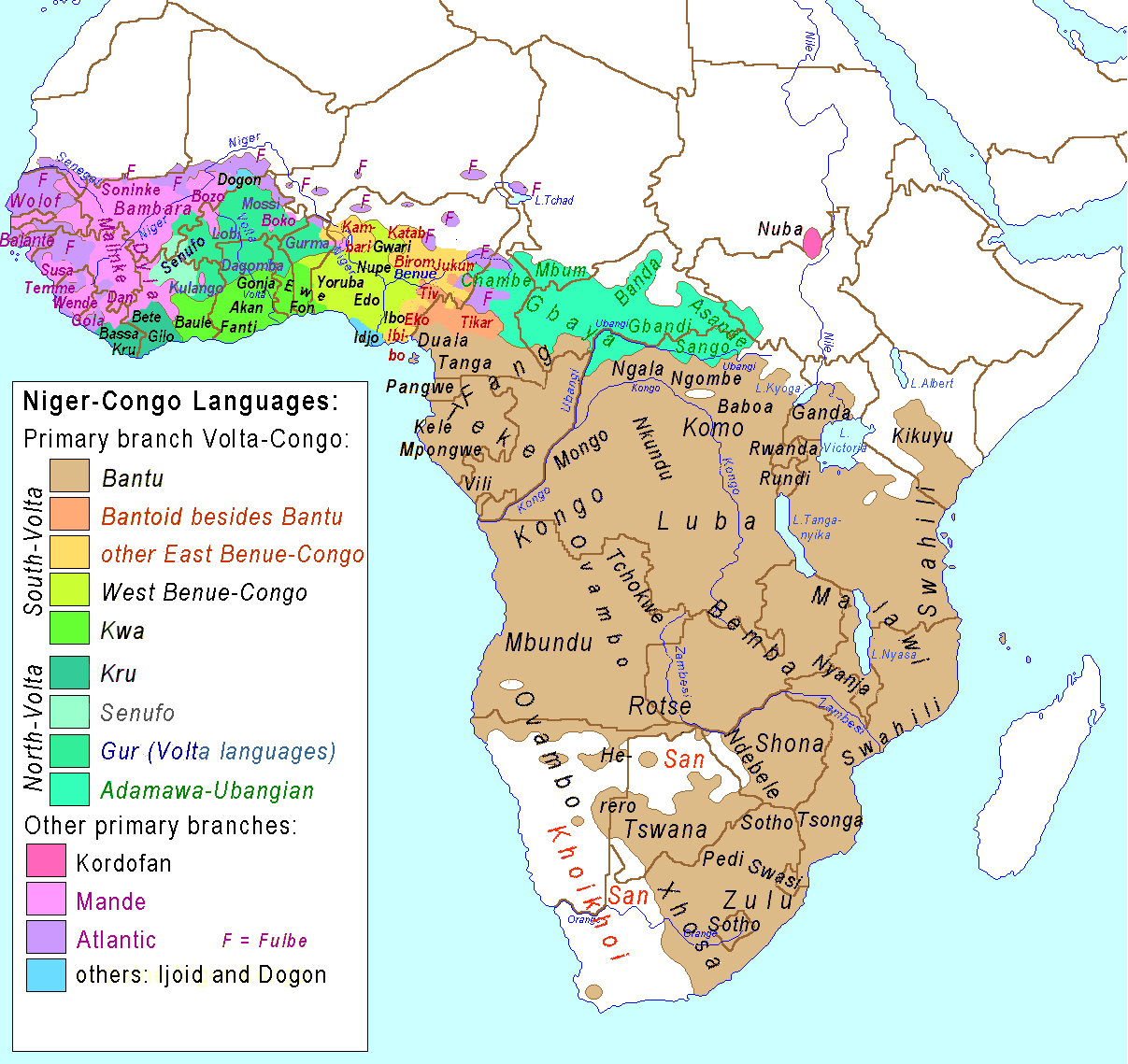
Bantu-speaking People Shape Linguistic and Cultural Landscape
Cultural Evolution
4 min read
Updated By: History Editorial Network (HEN)
Published:
The arrival of the Bantu-speaking people in South Africa reshaped the region's linguistic and cultural landscape. Traveling southwards over centuries, Bantu-speaking groups brought with them advanced agricultural techniques, iron tools, and a rich cultural heritage. This migration resulted in the assimilation of the indigenous Khoisan peoples and the formation of diverse societies.
The Bantu-speaking people introduced new crops such as millet, sorghum, and yams, significantly impacting the region's food production. Their knowledge of iron metallurgy revolutionized tool-making and trade practices. Moreover, their social structures, beliefs, and languages influenced the communities they interacted with, leading to a complex intermingling of customs and traditions.
The interaction between the Bantu-speaking people and the indigenous populations contributed to the development of unique societies with distinct cultural practices. This cultural fusion gave rise to diverse art forms, music styles, and spiritual beliefs that continue to shape South Africa's cultural identity to this day.
The linguistic impact of the Bantu migration was profound, as Bantu languages spread across the region, influencing the development of many present-day languages in South Africa. The incorporation of Bantu vocabulary enriched local dialects and contributed to the evolution of new linguistic variations.
Overall, the arrival of the Bantu-speaking people marked a transformative period in South Africa's history, laying the foundation for the rich tapestry of cultures and languages that define the country today. Their legacy endures in the customs, traditions, and languages of the diverse communities across the nation.
#BantuMigration #CulturalAssimilation #LinguisticDiversity
